Challenges and Pretreatment Optimization for RO in Wastewater and Greywater Reuse Projects| Insights by AQUALITEK
Reverse osmosis (RO) plays a critical role in advanced wastewater and greywater reuse, producing high-quality reclaimed water. However, wastewater presents unique challenges such as fouling, scaling, and organic loading. This article explores the main operational challenges and effective pretreatment strategies to ensure stable RO performance.
- Introduction
- Major Challenges in RO for Reclaimed Water
- 1. Severe Membrane Fouling
- 2. High Scaling Potential
- 3. Unstable Feed Water Quality
- 4. Biofouling and Microbial Regrowth
- Pretreatment Optimization Strategies
- 1. Multi-Barrier Pretreatment Configuration
- 2. Advanced Oxidation Processes (AOP)
- 3. Online Monitoring and Control
- 4. Chemical and Biological Pretreatment Integration
- Example: Typical RO Pretreatment Flow for Reclaimed Water
- Maintenance and Operational Best Practices
- Conclusion
Introduction
As global water scarcity intensifies, wastewater reuse and greywater recycling have become vital solutions for sustainable water management.
Reverse osmosis (RO), as the final polishing step, delivers ultrapure or industrial-grade reclaimed water, but its success largely depends on feed water quality and pretreatment efficiency.
Unlike traditional desalination, wastewater contains complex organic matter, suspended solids, nutrients, and microorganisms, making RO operation more difficult and maintenance-intensive.
Major Challenges in RO for Reclaimed Water
1. Severe Membrane Fouling
Wastewater contains colloids, organic macromolecules, and microbial residues, which easily adhere to the membrane surface, forming a dense fouling layer.
Consequences:
•Reduced water flux
•Increased pressure differential (ΔP)
•More frequent chemical cleaning
Key fouling types:
•Organic fouling: humic substances, surfactants, oils
•Colloidal fouling: clay, iron hydroxides, silica
•Biofouling: bacteria and extracellular polymeric substances (EPS)
2. High Scaling Potential
Reclaimed water often contains residual calcium, magnesium, silica, and phosphate ions, which can crystallize under concentration, especially in multi-stage RO systems.
Typical scales: CaCO₃, CaSO₄, BaSO₄, SiO₂
Impact:
•Increases system pressure
•Reduces permeate quality
•Shortens membrane life
3. Unstable Feed Water Quality
The quality of treated wastewater fluctuates with seasonal flow, industrial discharge, and biological treatment efficiency.
Impact:
•Sudden spikes in COD, turbidity, or ammonia load
•Unstable permeate conductivity
•Difficulties in maintaining recovery and flux balance
4. Biofouling and Microbial Regrowth
Even after biological treatment, residual microorganisms and nutrients can grow on membranes, forming biofilm and causing irreversible damage.
Complication: biofilm also protects other foulants, making cleaning less effective.
Pretreatment Optimization Strategies
A robust pretreatment system is the foundation of any successful RO wastewater reuse project.
1. Multi-Barrier Pretreatment Configuration
Design pretreatment to remove different contaminants step-by-step:
|
Stage |
Technology |
Purpose |
|
Coarse Screening |
Rotary drum filter / fine screen |
Remove large particles and fibers |
|
Coagulation–Flocculation |
PAC / polymer dosing |
Aggregate colloids and organics |
|
Sedimentation / DAF |
Clarify suspended solids |
Reduce turbidity and TSS |
|
UF / MF Membrane |
Ultrafiltration or microfiltration |
Barrier for microorganisms and colloids |
|
Activated Carbon / AOP |
Adsorption and oxidation |
Reduce organic load and odor |
|
Antiscalant + pH Control |
Chemical dosing |
Prevent scaling before RO |
2. Advanced Oxidation Processes (AOP)
Integrating ozonation (O₃), UV/H₂O₂, or Fenton oxidation before RO helps decompose refractory organics and destroy bioactive compounds.
Benefits:
•Decreases TOC and COD
•Minimizes biofouling potential
•Enhances membrane life
3. Online Monitoring and Control
Modern reclaimed water RO systems rely on real-time sensors to maintain stable operation:
•SDI (Silt Density Index): should be ≤3 before RO
•TOC and turbidity monitoring: ensure feed stability
•Automatic antiscalant dosing and pH adjustment for adaptive control
4. Chemical and Biological Pretreatment Integration
Combine physical, chemical, and biological processes for maximum contaminant removal:
•MBR (Membrane Bioreactor) + RO: the most common configuration
•Biofiltration + AOP + RO: ideal for industrial wastewater reuse
•UF + Activated Carbon + RO: compact solution for greywater reuse
Example: Typical RO Pretreatment Flow for Reclaimed Water
Flow Sequence:
Screening → Coagulation → Sedimentation → Ultrafiltration → Activated Carbon → Antiscalant + RO
Each step progressively removes pollutants that could damage or foul the RO membranes, ensuring stable flux and longer system life.
Maintenance and Operational Best Practices
•Perform CIP cleaning regularly (every 3–6 months)
•Keep SDI < 3, TOC < 2 mg/L, and turbidity < 0.5 NTU
•Periodically inspect UF membrane integrity
•Apply biocide dosing if microbial regrowth is detected
•Use low-fouling or high-rejection RO membranes for higher reliability
Conclusion
RO is an indispensable technology for producing high-quality reclaimed water, but wastewater’s complex composition brings challenges like fouling, scaling, and fluctuating feed quality.
Through optimized pretreatment, AOP integration, and smart monitoring, operators can ensure stable RO operation, reduce cleaning frequency, and achieve sustainable water reuse.




Request More Information or Expert Advice
Share a few details, and we’ll provide deeper insights, tailored suggestions, or product support.
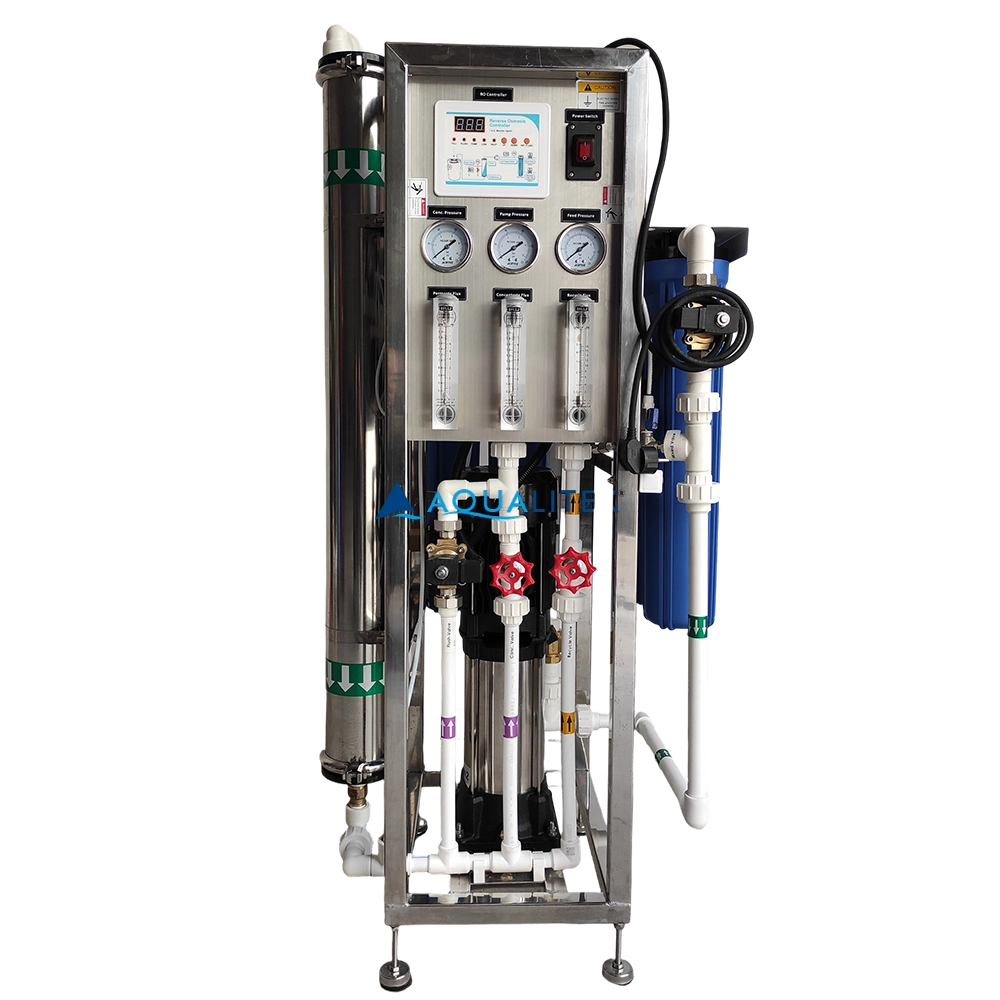

Our 500 LPH Reverse Osmosis (RO) System is engineered to provide high-quality purified water for commercial applications. Designed with advanced RO technology, durable components, and a user-friendly interface, this system ensures consistent performance, low maintenance, and long-term reliability.
With its compact design and robust skid-mounted frame, it’s an excellent choice for businesses that demand efficiency and quality in water purification.
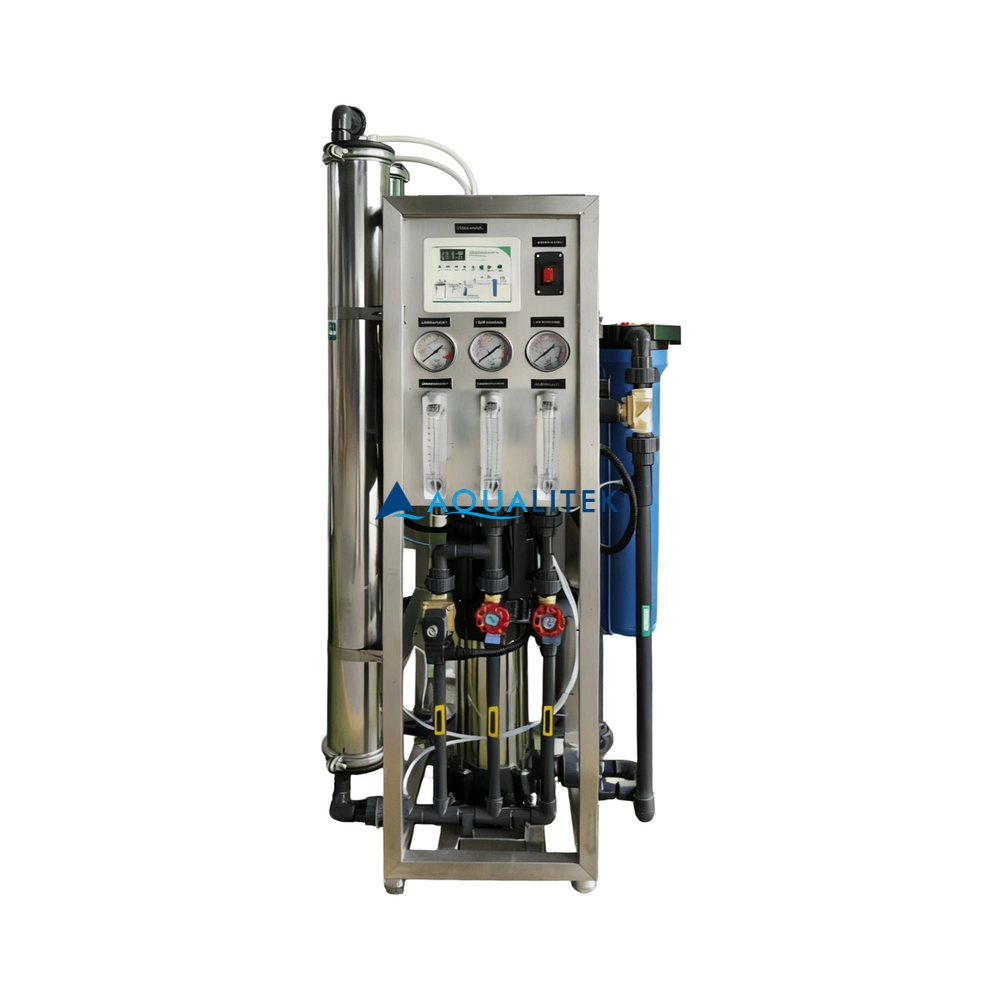

TWV series Reverse Osmosis (RO) systems are pre-engineered and pre-assembled units with 2.5”/4” membrane housings(single element type)for tap water(lower TDS).They are designed for overall superior performance, high recovery rates and offer great savings with low maintenance and operation costs.
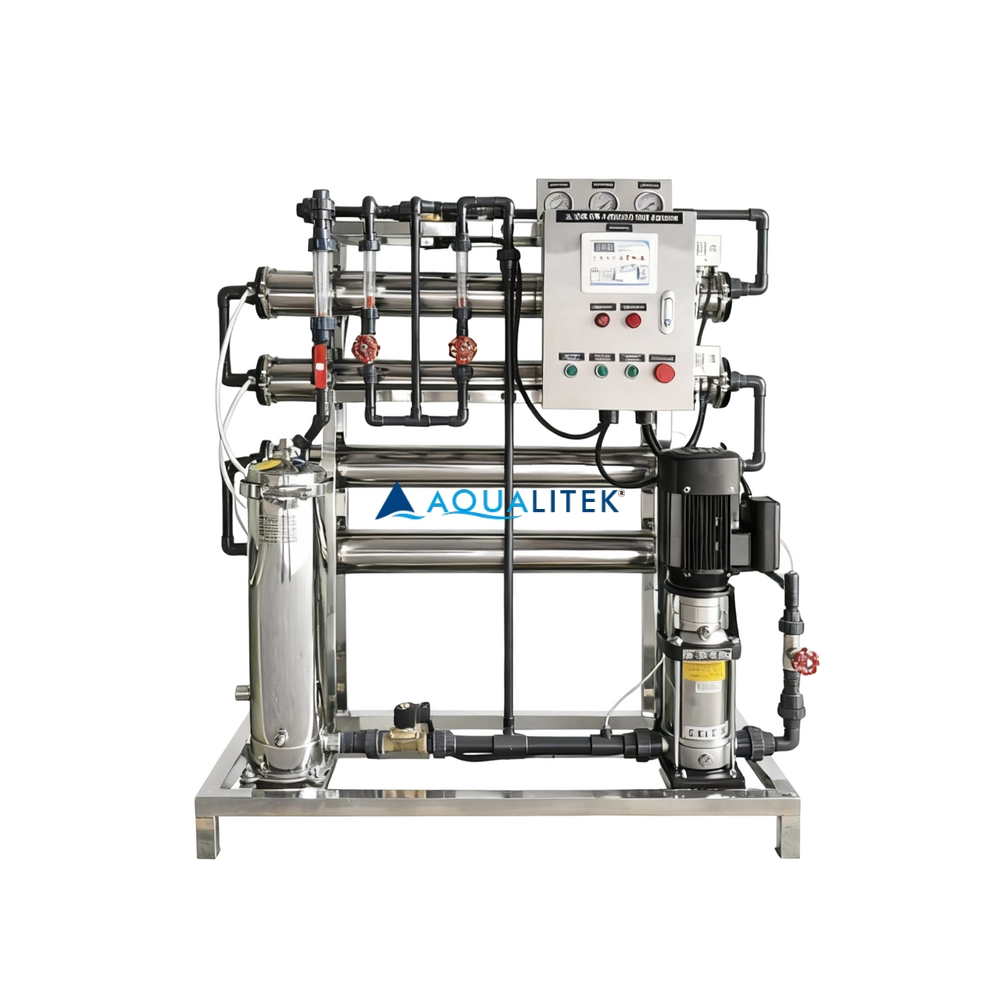

TWF series Reverse Osmosis (RO) systems are pre-engineered and pre-assembled units with 4” membrane housings(multiple elements type) for tap water(lower TDS) .The medium large volumes can help meet your a variety of commercial and industrial applications. They are designed for overall superior performance, high recovery rates and offer great savings with low maintenance and operation costs.
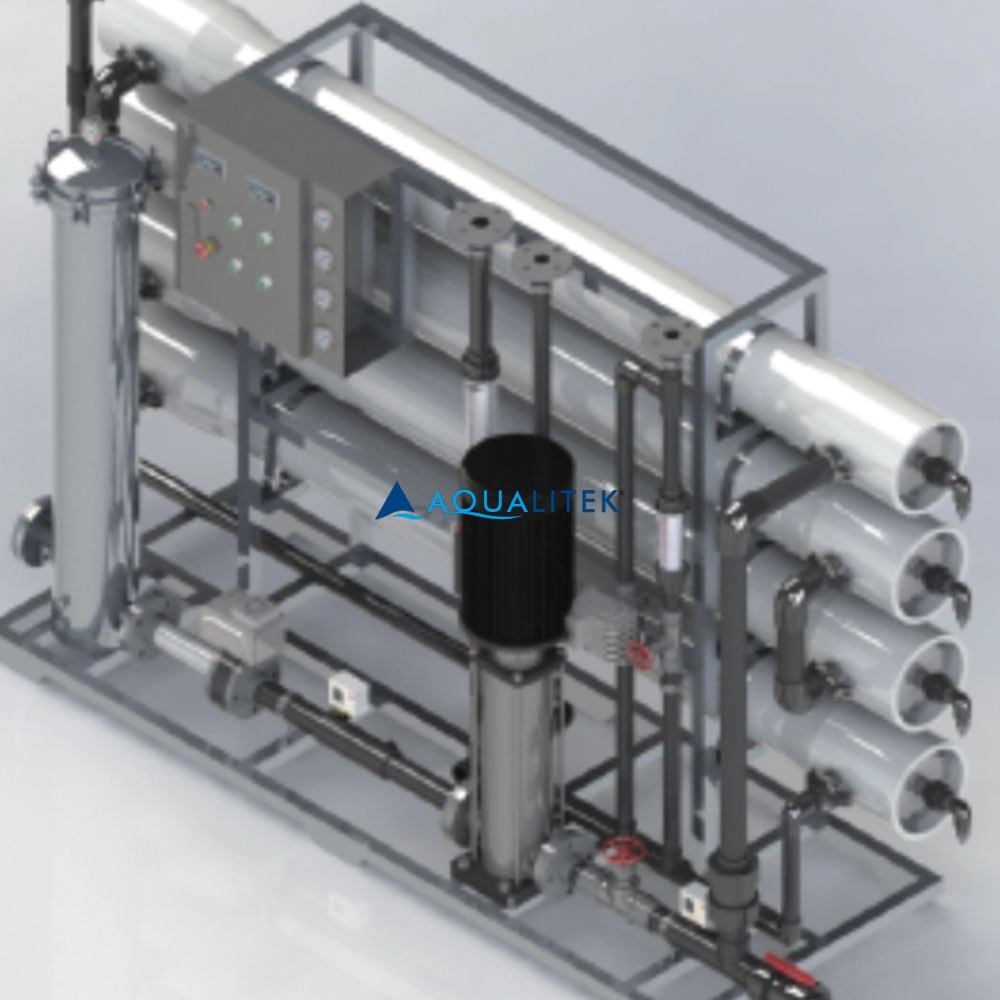
TWE series Reverse Osmosis (RO) systems are pre-engineered and pre-assembled units with 8” membrane housings for tap water (lower TDS). The large volumes can help meet your a variety of industrial applications. They are designed for overall superior performance, high recovery rates and offer great savings with low maintenance and operation costs.
© 2026 AQUALITEK. All rights reserved.




















AQUALITEK- Aimee Hoo
AQUALITEK - Aimee Hoo