Best Guide to Activated Carbon Adsorption: What It Removes and When to Regenerate or Replace It| Insights by AQUALITEK
Learn what pollutants activated carbon removes from water and when it should be regenerated or replaced. Explore how carbon filters improve water quality in residential, commercial, and industrial applications.
- What Pollutants Does Activated Carbon Adsorption Primarily Remove in Water Treatment? When Does It Need to Be Regenerated or Replaced?
- Understanding Activated Carbon in Water Treatment
- Pollutants Removed by Activated Carbon Adsorption
- When Does Activated Carbon Need to Be Regenerated or Replaced?
- Applications of Activated Carbon in Water Treatment
- Conclusion
What Pollutants Does Activated Carbon Adsorption Primarily Remove in Water Treatment? When Does It Need to Be Regenerated or Replaced?
Understanding Activated Carbon in Water Treatment
Activated carbon (AC) is one of the most effective and widely used adsorbents in water purification. Made from carbon-rich materials such as coconut shells, coal, or wood, it is processed to create a highly porous structure with a vast surface area — sometimes exceeding 1,000 m² per gram. This porous network allows activated carbon to trap and remove contaminants through a process known as adsorption.
Whether used in drinking water systems, industrial wastewater treatment, or municipal plants, activated carbon plays a vital role in improving taste, odor, and safety of water.
Pollutants Removed by Activated Carbon Adsorption
Activated carbon primarily targets organic contaminants and certain inorganic impurities that affect water quality. Below are the major types of pollutants it removes:
1.Chlorine and Chloramine
Activated carbon efficiently removes chlorine and chloramine commonly added during municipal water disinfection. This not only improves taste and odor but also protects sensitive downstream systems such as reverse osmosis membranes.
2.Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs)
VOCs such as benzene, toluene, xylene, and trichloroethylene are often found in industrial effluents. AC adsorbs these organic chemicals effectively, reducing toxicity and ensuring compliance with environmental discharge standards.
3.Natural Organic Matter (NOM)
NOM, including humic and fulvic acids, can react with chlorine to form harmful disinfection by-products (DBPs) like trihalomethanes (THMs). Activated carbon removes these precursors, preventing DBP formation.
4.Pesticides and Herbicides
Agricultural runoff often contains pesticides, insecticides, and herbicides. AC adsorption effectively captures these trace organic pollutants to produce cleaner and safer water.
5.Taste, Odor, and Color Compounds
Compounds such as geosmin, 2-MIB, and other organics are responsible for unpleasant tastes and odors in drinking water. AC efficiently eliminates these sensory issues, improving overall water quality.
6.Residual Pharmaceuticals and Micropollutants
With the growing concern over pharmaceutical residues and emerging contaminants, activated carbon — especially powdered activated carbon (PAC) — is increasingly used in advanced water treatment systems to remove trace-level pollutants.
When Does Activated Carbon Need to Be Regenerated or Replaced?
Over time, the pores of activated carbon become saturated with adsorbed pollutants, reducing its effectiveness. The timing for regeneration or replacement depends on water quality, system design, and usage conditions.
1.Signs It Needs Replacement or Regeneration:
•Decrease in contaminant removal efficiency (e.g., chlorine or odor returns).
•Reduced flow rate or pressure drop across the carbon bed.
•Higher levels of organic carbon detected in treated water (measured as TOC).
2.Typical Service Life:
•Granular Activated Carbon (GAC): Usually lasts 6–12 months in household filters and up to 2–3 years in industrial systems, depending on load.
•Powdered Activated Carbon (PAC): Used once and replaced frequently due to its fine particle size.
3.Regeneration Methods:
•Thermal Regeneration: Heating the saturated carbon at 800–900°C in an inert atmosphere to remove adsorbed organics.
•Steam Regeneration: Using steam to desorb lighter organics.
•Chemical Regeneration: Applying chemical reagents to dissolve or oxidize adsorbed pollutants.
In most residential and small commercial systems, it’s more economical to replace the carbon rather than regenerate it. Industrial plants, however, often regenerate AC to reduce operating costs and waste.
Applications of Activated Carbon in Water Treatment
•Drinking Water Purification: Removal of chlorine, taste, and odor compounds.
•Industrial Wastewater Treatment: Adsorption of organic pollutants and solvents.
•RO Pretreatment: Protecting membranes from chlorine damage.
•Aquaculture and Food Processing: Maintaining high water quality standards.
Conclusion
Activated carbon adsorption is a versatile, cost-effective, and environmentally friendly method for removing organic and chemical pollutants from water. It plays a critical role in both municipal and industrial water treatment systems, ensuring clean, safe, and pleasant-tasting water.
However, regular monitoring and timely replacement or regeneration of activated carbon are essential to maintain peak performance and ensure consistent water quality.
At Aqualitek Water Treatment Technologies Co., Ltd., we provide a full range of activated carbon filters, adsorption systems, and regeneration solutions, tailored to meet diverse water purification needs across residential, commercial, and industrial applications.



Request More Information or Expert Advice
Share a few details, and we’ll provide deeper insights, tailored suggestions, or product support.

Our 500 LPH Reverse Osmosis (RO) System is engineered to provide high-quality purified water for commercial applications. Designed with advanced RO technology, durable components, and a user-friendly interface, this system ensures consistent performance, low maintenance, and long-term reliability.
With its compact design and robust skid-mounted frame, it’s an excellent choice for businesses that demand efficiency and quality in water purification.

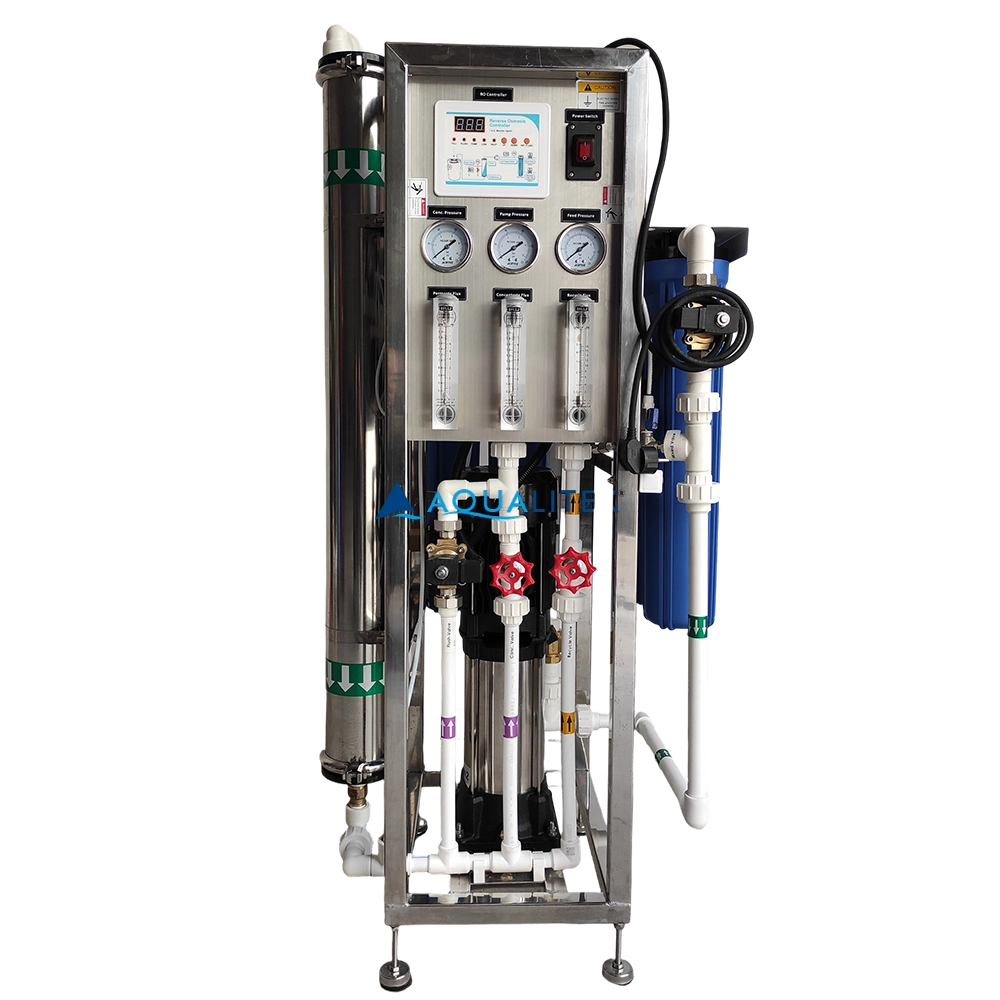
TWV series Reverse Osmosis (RO) systems are pre-engineered and pre-assembled units with 2.5”/4” membrane housings(single element type)for tap water(lower TDS).They are designed for overall superior performance, high recovery rates and offer great savings with low maintenance and operation costs.

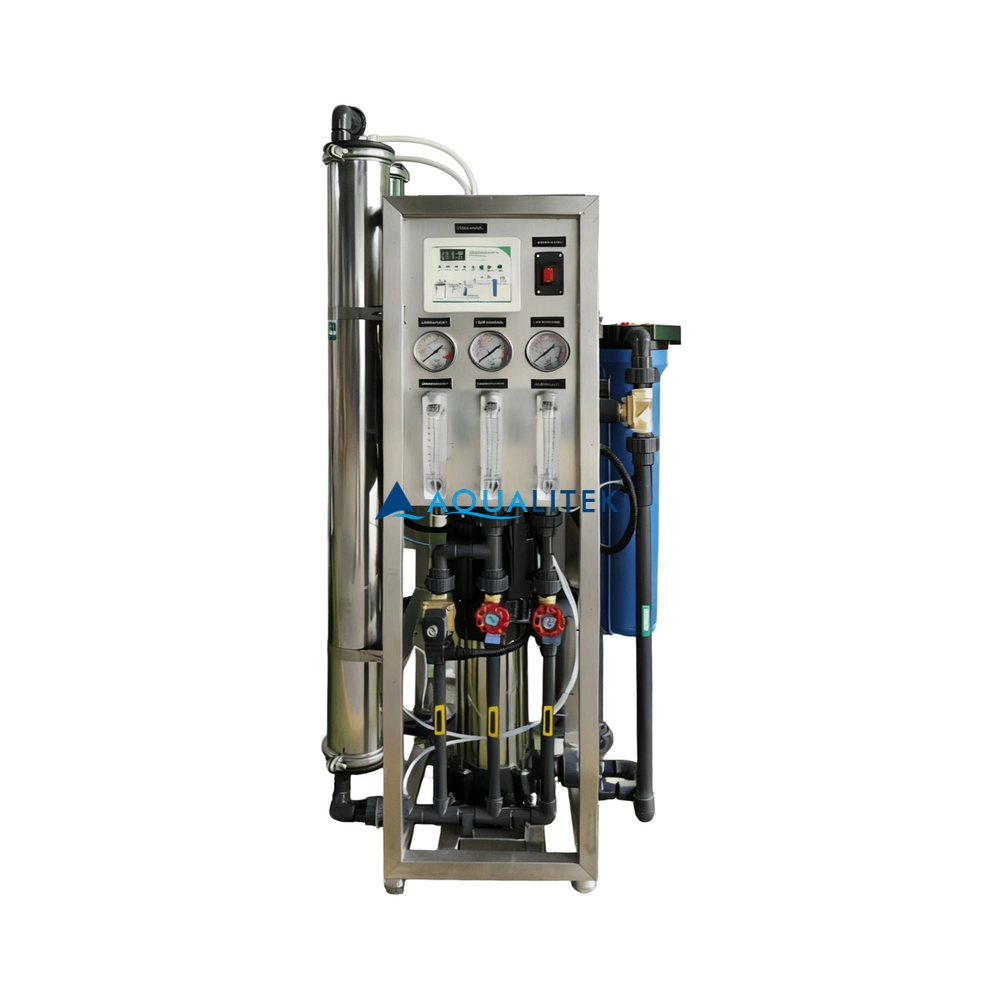
TWF series Reverse Osmosis (RO) systems are pre-engineered and pre-assembled units with 4” membrane housings(multiple elements type) for tap water(lower TDS) .The medium large volumes can help meet your a variety of commercial and industrial applications. They are designed for overall superior performance, high recovery rates and offer great savings with low maintenance and operation costs.

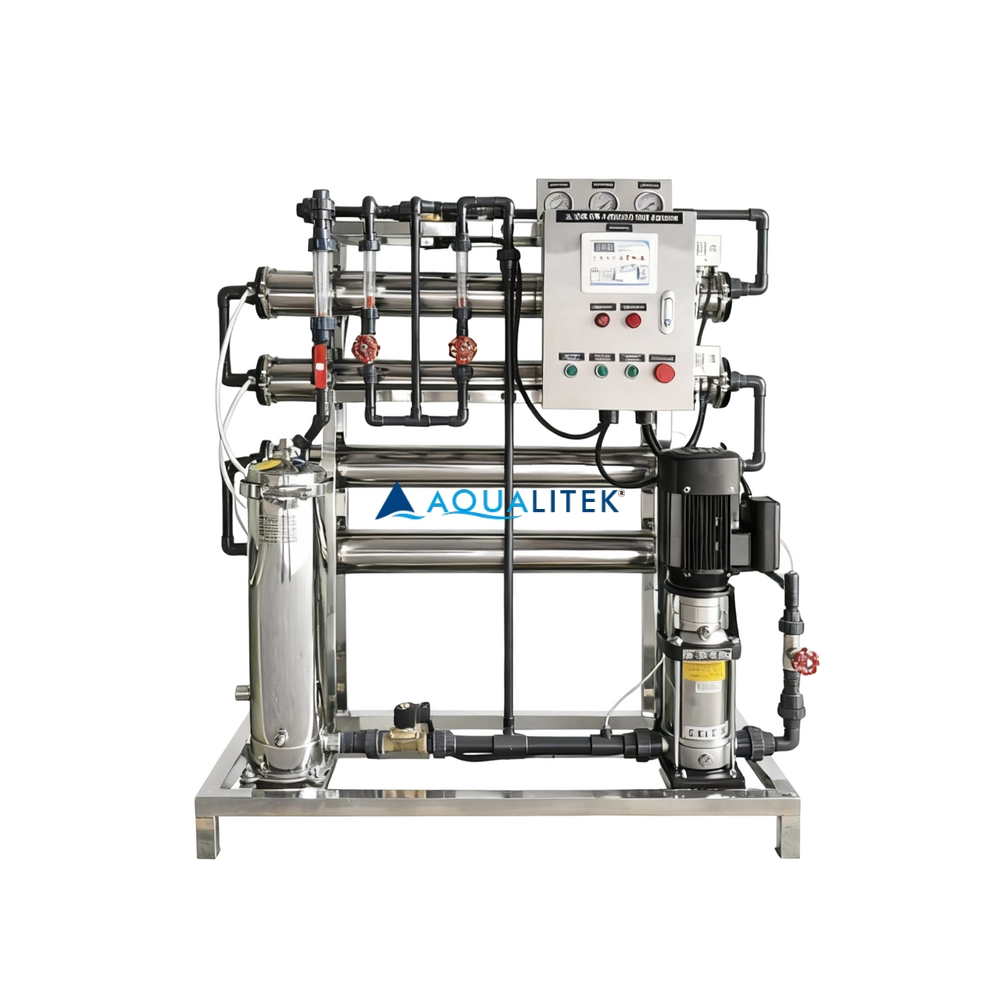
TWE series Reverse Osmosis (RO) systems are pre-engineered and pre-assembled units with 8” membrane housings for tap water (lower TDS). The large volumes can help meet your a variety of industrial applications. They are designed for overall superior performance, high recovery rates and offer great savings with low maintenance and operation costs.
© 2026 AQUALITEK. All rights reserved.





















AQUALITEK- Aimee Hoo
AQUALITEK - Aimee Hoo